Former Projects
This project is a cooperation work together with the laboratory for micro cutting (LFM) and institute for electric drives (IALB) at the University of Bremen. Central idea of the projects is the development of a mircoscopic axis-less grinding tool.mehr...
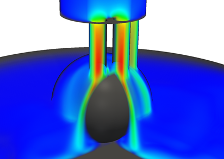
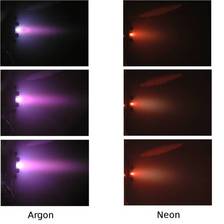
Just as in an arc welder, a high-current electric arc is struck between the anode and cathode. As the cathode heats up, it emits electrons, which collide with and ionize a propellant gas to create plasma in MPD thruster. For gases, there are many circumstances where the electron temperature Te differs from the heavy particle ( ions and neutral atoms) temperature Th.mehr...
Total fuel mass is one of the main economical and technical restrictions while designing space propulsion systems. Given the high costs related to the transport of mass into space, the total fuel mass necessary for accomplishment of the mission should be minimized. An optimum “thrust/fuel consumption ratio” demands the maximization of the gas exit velocity for a given mass flow.mehr...
One of the most amazing applications of magneto fluid dynamics are astrophysical approximations. High temperatures are responsible for fusion and ionization processes in space. Furthermore, the motion of charged particles in space is part of its astrophysical description. The motion of charged particles near planets with a magnetic core or inside accretion discs in the environment of a black hole is the result from attaching forces of other particles and is influenced by electric and magnetic fields.mehr...
When the difference in electric potential between electrodes with different charge is high enough, an electric discharge through the fluid medium separating the electrodes occurs. The resulting electric flux is associated with a local motion of electrons, the only mobile charge carrier inside the solid electrodes. As a result from the motion of electrons, the only mobile charge carrier inside the solid electrodes.mehr...
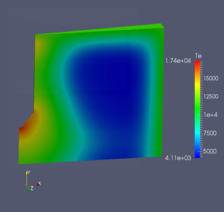
When developing machines and facilities with optimization regarding fluid dynamic behavior, the form of the optimization tools results from the operating conditions of the studied flow (laminar, turbulent, incompressible, trans-sonic, hyper-sonic, molecular, continuous etc.). If mixed conditions are present, the interactions between the sub-models has to be investigated and modeled through coupled transport equations.mehr...
The computational description of evaporation processes requires the calculation of the heat and mass transfer exchange rate over the liquid/gas interface. The most influential parameter for the exchange rates is the relative humidity of the gas phase. The highest relative humidity gradient occurs at temperature levels slightly below the boiling point.mehr...
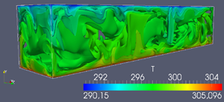
Hurricanes are effected by turbulent natural convection flows, which are caused by solar radiation. To understand the hydrodynamic stability of these flows, especially in terms of the Coriolis acceleration of the earth rotation, the first step is an investigation of a simplified convection problem. mehr...
It is proposed to establish a Collaborative Research Centre (SFB) with the title “Autonomous Lunar Infrastructures (ALI)” at University of Bremen with several cooperating partners close by. Bremen is an important site in Germany where space related activities are concentrated with more than 1500 engineers and scientists working in the fields of development, production, operation and utilisation of orbital and exploration systems, satellites and launchers.mehr...
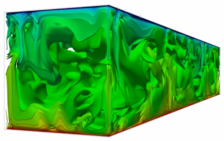
Thermally driven flows are described as a turbulent compressible Rayleigh-B´enard problem. For the numerical discretisation of the Large-Eddy-Simulation the flow is separated in large and small scales, the so-called sub-grid scales.mehr...
This set-up forces a debris flow at the groung of the cylinder. Additionally the interface between debris and liquid media is destabilized. The new steady shifting form depends on debris material and the mean shear stress at the surface of the granular bed.mehr...
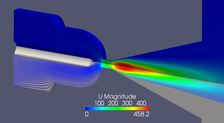
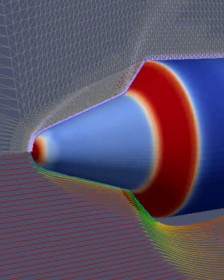
The subject of interest is the validation of a 3-D numerical computer model of a hypersonic flow around double cone geometry. The double cone geometry represent a generic space vehicle which enters an atmosphere with very high velocity.mehr...
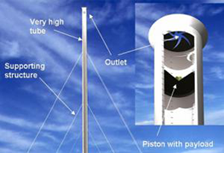
The objective of this study is to prove the feasibility of the suggested technical concept and validate the elementary performance calculations. Besides gas- and thermodynamic analyses, this includes basic examinations on some options for the supporting structure;mehr...








 "
"